best least expensive way to test for testicular torsion|testicular torsion physical examination : dealers We'll explore the various severity levels of testicular torsion, break down the costs of diagnostic procedures, imaging tests, medications, and surgical interventions, and . LIVE RTP JNT777. JNT777 merupakan bandar SLOT, LIVE CASINO dan SPORTBOOK terpercaya di Indonesia. Partner resmi dari ratusan provider terbaik di dunia.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Escolha algumas delas e comece a jogar. 6. Cruzadas Clube. Aproveite esse site que possui mais de 700 palavras cruzadas gratuitas e de fácil acesso. Basta você escolher .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding.
POCUS provides real-time analysis of return of blood flow and can thus guide further rotation, or opposite direction rotation, as needed. Introduction. Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency with a yearly incidence of 3.8 per 100,000 . We'll explore the various severity levels of testicular torsion, break down the costs of diagnostic procedures, imaging tests, medications, and surgical interventions, and .Testicular torsion typically presents with unilateral scrotal pain that begins suddenly. Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and vomiting,. Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or .
1st tests to order. Testicular Workup for Ischemia and Suspected Torsion (TWIST) score; gray-scale ultrasound; power Doppler ultrasound; color Doppler ultrasound Introduction. Scrotal complaints are relatively common in the emergency department, comprising at least 0.5% of all emergency department visits. Testicular torsion .Diseases & Conditions / Testicular Torsion. Testicular torsion is a painful condition where your testicle twists and loses its blood supply. It requires emergency care. If the blood supply .
ultrasound for testicular torsion
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . Additional diagnostic methods include urine tests to exclude infection, scrotal ultrasound (color Doppler) showing absent or decreased blood flow to the affected testicle, or even surgery to explore the area and confirm .How is testicular torsion diagnosed? Diagnosis entails a physical examination and a complete medical history. A prompt diagnosis is imperative because prolonged testicular torsion may cause irreversible damage to the testes. Other diagnostic tests may be done, but there is no test that diagnoses testicular torsion accurately all the time. The only way to prevent testicular torsion is to have surgery to attach your testicles to the insides of your scrotum, but this is only done if you have already had torsion or are currently having it.
Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 18. Previous testicular torsion. If you've had testicular pain that went away without treatment (intermittent torsion and detorsion), it's likely to occur again. The more frequent the bouts of pain, the higher the risk of testicular damage. Family history of testicular torsion.
Testicular torsion can occur at any age. Testicular torsion can occur at any age, but it is primarily associated with a bimodal distribution in the first year of life and in adolescence. Although exceedingly rare, there are case reports of testicular torsion occurring in .rgency surgical exploration to salvage the testis. The assessment of patients with acute scrotal pain is done mainly using color Doppler ultrasonography, which, however, requires skills and has limitations of being highly operator-dependent and uncomfortable to patients with scrotal pains because it may take too long to perform and often involves probe compression. Scrotal . Testicular torsion is a serious condition. If not treated within hours, it can lead to blood flow loss that may require the testicle to be removed. . There are two ways that the condition can be repaired: Manual detorsion: This is when the healthcare provider grasps the testicle and rotates it within the scrotum in an outward direction one to . Under certain circumstances, a testicular cancer or tumor can present with symptoms similar to a testicular torsion. This occurs because there may be some bleeding into a testis cancer that can cause the same type of pain and swelling as a torsion of the testis. An ultrasound test to examine the contents of the scrotum may help sort out the cause.
↑ Blaivas, M, et al. Emergency evaluation of patients presenting with acute scrotum using bedside ultrasonography. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2001; 8(1):90-93. ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8. ↑ Gordon J, Rifenburg RP. . Spermatic Cord . Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic Test for Testis Torsion in Pediatric Acute Scrotum: A Prospective Comparison to Gold Standard Diagnostic Test Study. J Urol .Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours . See a doctor right away if you think you have .
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become . Introduction. Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord and its contents twists within the tunica vaginalis, compromising the blood supply to the testicle.. Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency, as without treatment the affected testicle will infarct within hours.Whilst theoretically it can occur at any age, peak incidence is in neonates and . Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicle and preserving future fertility. . Laboratory tests are unlikely to be of consequence, as no single test .
Testicular torsion may also run in families. Other causes. Testicular torsion can occur at any time – e.g. while sleeping, sitting on the couch, or after activity and trauma. Rapid growth of the testicles during puberty is also a risk factor. Who is at risk of testicular torsion? Most cases are between the ages of 12 and 18, but testicular . Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage. Find out what causes this . Scrotal complaints are relatively common in the emergency department, comprising at least 0.5% of all emergency department visits. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to evaluate the .
Testicular torsion is a very serious condition and is considered a medical emergency. Rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord can cause obstruction of the arterial blood flow to the testicle, as well as the venous . This is called testicular torsion. If testicular torsion occurs, it requires urgent medical attention. What causes testicular torsion and who is at risk? Testicular torsion can happen to boys and men of any age, but most cases occur in . Testicular torsion, in which the spermatic cord becomes twisted resulting in ischaemia of the testicle, is a medical emergency. 1,2 It is vital that clinicians are able to recognise this condition and facilitate prompt surgical intervention, as complications can include necrosis and loss of the affected testis. 2 Although it is possible for testicular torsion to occur at any .
Testicular torsion in a baby happens when the sac around the testicles doesn’t attach to the scrotum. Which children are at risk for testicular torsion? Testicular torsion often occurs in boys ages 10 and older. It can also happen when a baby is growing in the mother's uterus, or shortly after a baby is born. The condition is sometimes seen .
American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, hernia, scrotal trauma, testicular torsion, testicular tumor, and torsion of testicular appendices. Testicular torsion describes a condition in which a testicle becomes twisted within the scrotum, causing the blood supply to the testicle to become blocked. Without sufficient blood flow, the testicle can die due to lack of oxygen and, in severe cases, may need to be removed. Therefore, suspected testicular torsion should be treated as a medical emergency.testicles more likely to twist. There is no way to know for sure who will develop torsion. Who gets testicular torsion? Males of any age can get it, but it happens most often in newborns and .2 Contents 1 Foreword 2 2 Summary of key pathway components 3 3 Testicular torsion pathway 3 3.1 Raising awareness 4 3.2 Referral pathways 4 3.3 Assessment, including TWIST score & ultrasound 5 3.4 Surgery 6 3.5 Follow up 6 3.6 Revalidation & maintaining skills 6 4 Patient experience 7 5 Audit points & areas for further research 8 6 Resources & further information 8
Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and definitive management are the keys to avoid testicular loss. All prepubertal and young adult . Consider the diagnosis of testicular torsion in all patients with acute testicular pain; Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency that requires immediate urologic consultation to increase the rate of tissue salvage. History, physical examination and ultrasound are all flawed in making the diagnosis. The gold standard is surgical exploration
More severe torsion requires more urgent treatment. The patient's age, health, and medical history may also determine the best course of treatment. In some cases, untwisting the testicle without surgery may be possible, although swelling and pain in the scrotum makes this unlikely. Surgery is the usual method for treating testicular torsion.
testicular torsion treatment
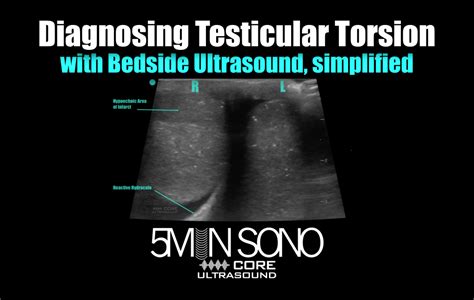
testicular torsion test results
compression test on wood theory
Resultado da 22 de abr. de 2021 · O Grupo Noticiário é formado por portais de notícias, rádios, jornais, blogs e revistas parceiras. Saiba mais.
best least expensive way to test for testicular torsion|testicular torsion physical examination